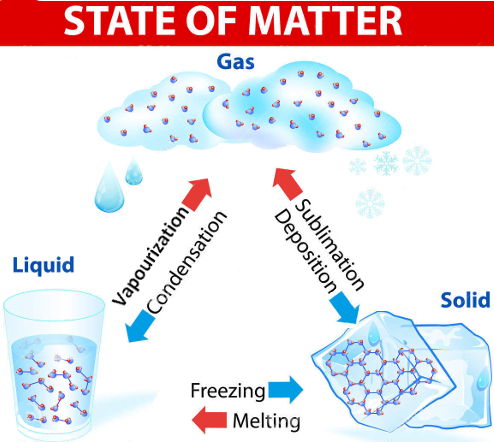
| Change of State | From | To | Heat Added or Removed |
| Melting | Solid | Liquid | Added |
| Freezing | Liquid | Solid | Removed |
| Vapourization | Liquid | Gas | Added |
| Condensation | Gas | Liquid | Removed |
| Sublimation | Solid | Gas | Added |
| Deposition | Gas | Solid | Removed |
THE SIX CHANGES OF STATE
|
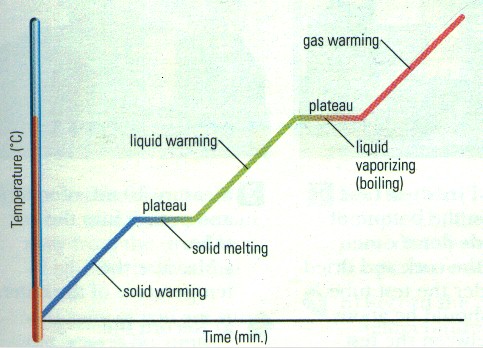
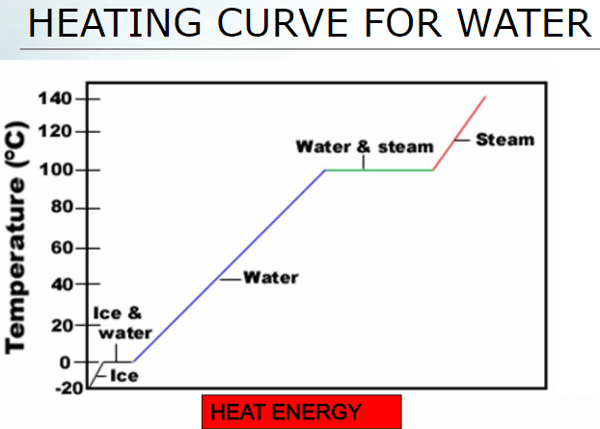
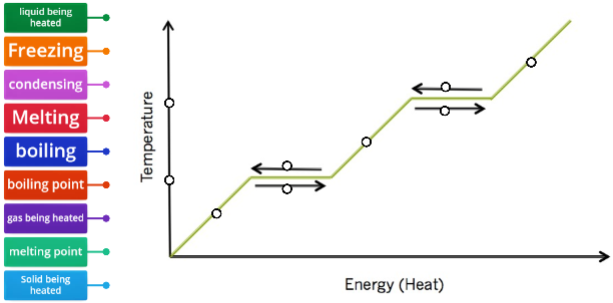
MELTING: change from a solid to a liquid. VAPOURIZATION: change from a liquid to a gas. Slow vapourization is called EVAPOURATION.Fast vapourization is called BOILING. CONDENSATION: change from a gas to a liquid.SOLIDIFICATION / FREEZING: change from a liquid to a solid.SUBLIMATION: change from a solid directly to a gasDEPOSITION: change from a gas directly to a solid |


| Change of State | From | To | Heat Added or Removed |
| Melting | Solid | Liquid | Added |
| Freezing | Liquid | Solid | Removed |
| Vapourization | Liquid | Gas | Added |
| Condensation | Gas | Liquid | Removed |
| Sublimation | Solid | Gas | Added |
| Deposition | Gas | Solid | Removed |
 PROPERTIES OF STATES OF MATTER
PROPERTIES OF STATES OF MATTER
|
What happens when you add heat to ice? Does the temperature rise
suddenly?
What happens when you add heat to water that is already 100°C?
Does the temperature rise?
A. Solid to Liquid
When you add heat to ice at 0°C, the temperature does not rise: